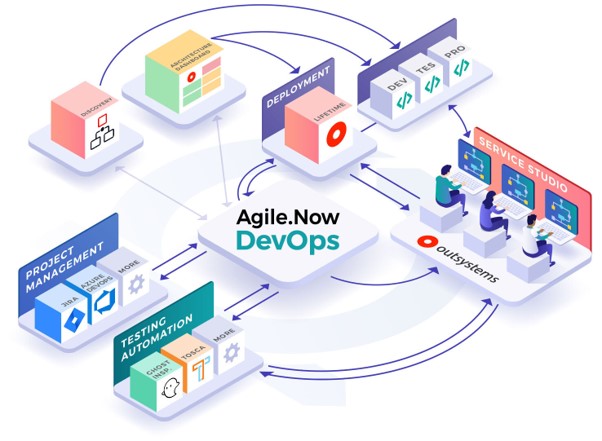
The Agile.now Factory application tie together existing tools and scales up the productivity of low-code projects throughout the entire execution process from software design, specification, development, testing to deployment and production. Agile.Now software integrates with several different systems and combines them into one process.
Project management tool
We recommend that you use one of the suggested project management tools alongside Agile.Now Factory. The PM tool defines the steps for automatic publishing and testing thereby enabling automated project workflow and helps us achieve the real DevOps process. Integrating a PM tool such as Azure DevOps or JIRA is mandatory without which we cannot execute Agile.Now Factory.
Integration & unit testing
Integrating a unit testing tool is optional but we highly recommend having them integrated as it forms an integral part of the overall DevOps pipeline. OutSystems provides two different types of Testing frameworks which can be integrated with the Agile.Now Factory application.
- Integration and unit tests for the server side: These unit tests are created using the OutSystems BDD testing framework (ver 1.4.0). You can download the software from OutSystems Forge from here.
- Integration and unit tests for client side: These unit tests are created using OutSystems BDD Framework for Client Side( Reactive and Mobile applications) and more information about this could be found here.
Integration and unit testing ensures the quality of the code developed through OutSystems. One of the advantages of Agile.Now Factory unit testing integration is the intelligent synchronization of unit tests from one environment to another. The tests are also synced for those issues that has been completed and deployed from one environment (for eg: Development) to another (for eg: Testing).
System testing
Automation testing is one of the most important starting point for the application quality assurance. The testing includes several different test case styles such as the unit, integration and use case testing. Performance testing is, of course, part of a comprehensive testing strategy and should be carried out with a separate software. This process is however optional, but we recommend integrating one of the many automation testing tool such as Ghost Inspector or Tosca. Recommendation is write and execute end to end test after deploying to test environment to avoid version issues.
OutSystems Lifetime
The DevOps is based on the OutSystems Lifetime for releases and management and is part of the OutSystems software. Lifetime is the centralized console for managing your OutSystems environments, applications, IT users, and security, covering the full application life cycle from development to deployment. More information about OutSystems lifetime can be found here.
Integration and data synchronization
The table below describes briefly about the data synchronization at various scenarios within the DevOps pipeline and the internal and external tools responsible for this:
Factory data
This details about the data flow that happens between the entities of the OutSystems Lifetime and Agile.Now Factory.
Note: Mandatory
| Entity | The owner of the data | Sync direction | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Environments | OutSystems Lifetime | from Lifetime to DevOps | The environments of infrastructure. The lifetime owns the environments and DevOps uses this information to manage deployments. |
| Users | OutSystems Lifetime | from Lifetime to DevOps | All users of infrastructure. The lifetime owns the users and DevOps uses this information to manage authentication. and authorization. |
| Teams | OutSystems Lifetime | from Lifetime to DevOps | All teams of infrastructure. The lifetime owns the teams and DevOps uses this information to manage project structures. The team must include a user in order for it to appear on the DevOps. |
| Team users | OutSystems Lifetime | from Lifetime to DevOps | Relation between the team and the user. The lifetime owns the team users and DevOps uses this information to manage authorizations. |
| Roles | OutSystems Lifetime | from Lifetime to DevOps | Roles that exist in the infrastructure. The lifetime owns the roles and DevOps uses this information to manage authorizations. |
| Environment accesses | DevOps | Internal auto generated | Environment accesses that exist in the infrastructure. A data structure that defines users' rights to the environment. Database information is built dynamically when a user logs in. |
| Applications | OutSystems Lifetime / Probe | from Lifetime to DevOps | Applications that exist in the infrastructure. The lifetime owns the applications and DevOps uses this information to manage deployments. Probe adds information from the development environment to make the process as efficient as possible. The application must include a team in order for it to appear on the DevOps.; |
| Modules | OutSystems Lifetime / Probe | from Lifetime to DevOps | Modules that exist in the infrastructure. The lifetime owns the modules and DevOps uses this information to manage deployments. Probe adds information from the development environment to make the process as efficient as possible. The module must include a team in order for it to appear on the DevOps. |
| Settings | DevOps | internal | Setting of a given infrastructure. |
Project data
This details about the data flow that happens between the entities of the project management tool such as JIRA or Azure and the Agile.Now Factory.
Note: Mandatory
| Entity | The owner of the data | Sync direction | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Project | Project management tool | from PM to DevOps | Project is a collection of issues. Used to coordinate the development of a product and tracking. The project management tool owns the projects and DevOps uses this information to link the projects, teams and issues together. |
| Project Modules | OutSystems / Project management tool / Factory | two-way | Modules are subsections of a project. Used to group issues within a project into smaller parts. The modules are owned by the OutSystems platform and are synchronized with the project management tool. The project modules must include a team in order for it to appear on the Factory. |
| Project issue statuses | Project management tool | from PM to DevOps | Status indicates the issue current place in project's workflow. The project management tool owns the status of the issue, and DevOps uses this information to configure and execute workflows. |
| Project issue types | Project management tool | from PM to DevOps | Stores various types of issues such as Epic, Story, Task, Bug. The project management tool owns the issue types, and DevOps uses this information to link the issues. |
| Project processes | DevOps | internal | Process process indicates the issues project workflow. DevOps owns the processes in the project and the user defines the steps for the process in DevOps. |
| Project settings | DevOps | internal | Configuration for statuses which should trigger an action. The DevOps owns the settings. |
| Project teams | DevOps | internal | Relation between the team and the project. The DevOps owns the project teams. |
| Project versions | Project management tool | from PM to DevOps | Versions represents point in time for a project. Issues can be assigned to a specific version to organize sprints around completing work in that version. The project management tool owns the versions of the project, and DevOps uses this information to define and execute workflows, tests and deployments. |
| Issues | Project management tool | two-way with PM and Factory | Issues are building blocks of a project. An issue could be a story, bug, task or other type. The project management tool owns the issues of the project, and DevOps uses this information to define and execute workflows, tests and deployments. The issue must include a Factory project, module, issue type and version in order for it to appear on the Factory. |
| Issue modules | Project management tool | two-way with PM and Factory | Stores the relation between issues and modules. Modules can be added in project management tool or Factory. The issue must include a module in order for it to appear on the Factory. |
| Issue history | DevOps | Internal auto generated | The table contains the change history of the issue. Logs are also written for a status change if the issue is manually or automatically moved in the project management tool. |
| Issue versions | Project management tool | from PM to DevOps | Represents relation between issue and version. The project management tool owns the issue versions and DevOps uses this information to define and execute workflows, tests and deployments. The issue must include a version in order for it to appear on the dashboard. |
| Issue test applications | DevOps | internal | Application Tests with independent unit tests that are connected with the different issues manually in the PM tool. The application tests are associated with an issue through modules. For eg: A module is added to an issue and necessary application tests are added to that module. |
Unit testing data
This details about the data flow that happens between the BDD Test environment integrated from the OutSystems forge and the Agile.Now Factory.
Note: Optional.
| Entity | The owner of the data | Sync direction | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tests | DevOps / Probe | two-way between BDD and DevOps | Tests that exist in the infrastructure within BDD. These tests are from the development environment. Sync automatically skips pages named; InternalError, Login, InvalidPermissions, NoPermission, MyInfo, NoTest% (e.g. NoTest_MyDemoPage) |
| Test executes | DevOps | real time | This involves with the test execution plan that would test the different test suits from every environment except the production environment |
| Test results | DevOps | real time | Result of execution of tests within the environment where the application tests and unit tests within that application tests were executed. |
End-to-end testing data
This details about the data flow that happens between the UI testing environment such as Ghost or Tosca and the Agile.Now Factory.
Note: Optional.
| Entity | The owner of the data | Sync direction | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tests | Automation testing tool | two-way between ATT and DevOps | Tests that exist in the infrastructure. All of the test are same no matter the environment. |
| Test executes | Automation testing tool | from ATT to DevOps | Test execution plans many test from DEV/TES/UAT environments. All of the test under application will be run. This involves the test execution plan that would test the different test suits from every environment except the production environment. All test will be executed no matter is code is ready or not. |
| Test results | Automation testing tool | from ATT to DevOps | Result of execution within the environment where the test suite and tests within that suite were executed. |
| Teams | DevOps | from DevOps to ATT | Sync from DevOps to auto test tool. Structure of teams auto generated from DevOps to Auto Testing Tool |
| Applications | DevOps | from DevOps to ATT | Sync from DevOps to auto test tool. Only application with "Set as home" flag is set as the home application (end user application) when the deployment is completed. .png) |